Photo by Anders Jildén on Unsplash
HowTo configure Proxmox VE 7.1 - Architecture & Monitoring
understand some key Proxmox concepts to help you design better systems
Proxmox has been architected masterfully. Simply put it consists of a three tier concept:
- The Datacenter, which can be one-node or multi-node cluster
- The Node, which is a physical bare-metal server running Proxmox VE
- The hosted systems or guests, which are the VMs and CTs running on the nodes
All three tiers above have common layers, with separate configuration for every tier, as follows:
- CPU, the processor(s)
- RAM, the main memory
- DISK, the storage (my advice use SSDs - NVMe 1st choice or SATA3 2nd choice - for everything; DO NOT use HDDs unless there is absolutely no other choice, even for backups)
- NET, the Network Interfaces(s), like NICs, DNS, etc
- FW, the Firewall
- SEC, Security - accounts & certificates
- HA, High Availability (redundancy, replication, backup, failover)
- MON, Monitoring & Logs of the layers above
The three most important official document describing Proxmox VE in detail are:
> Proxmox VE Documentation Index <
> Proxmox VE Release History <
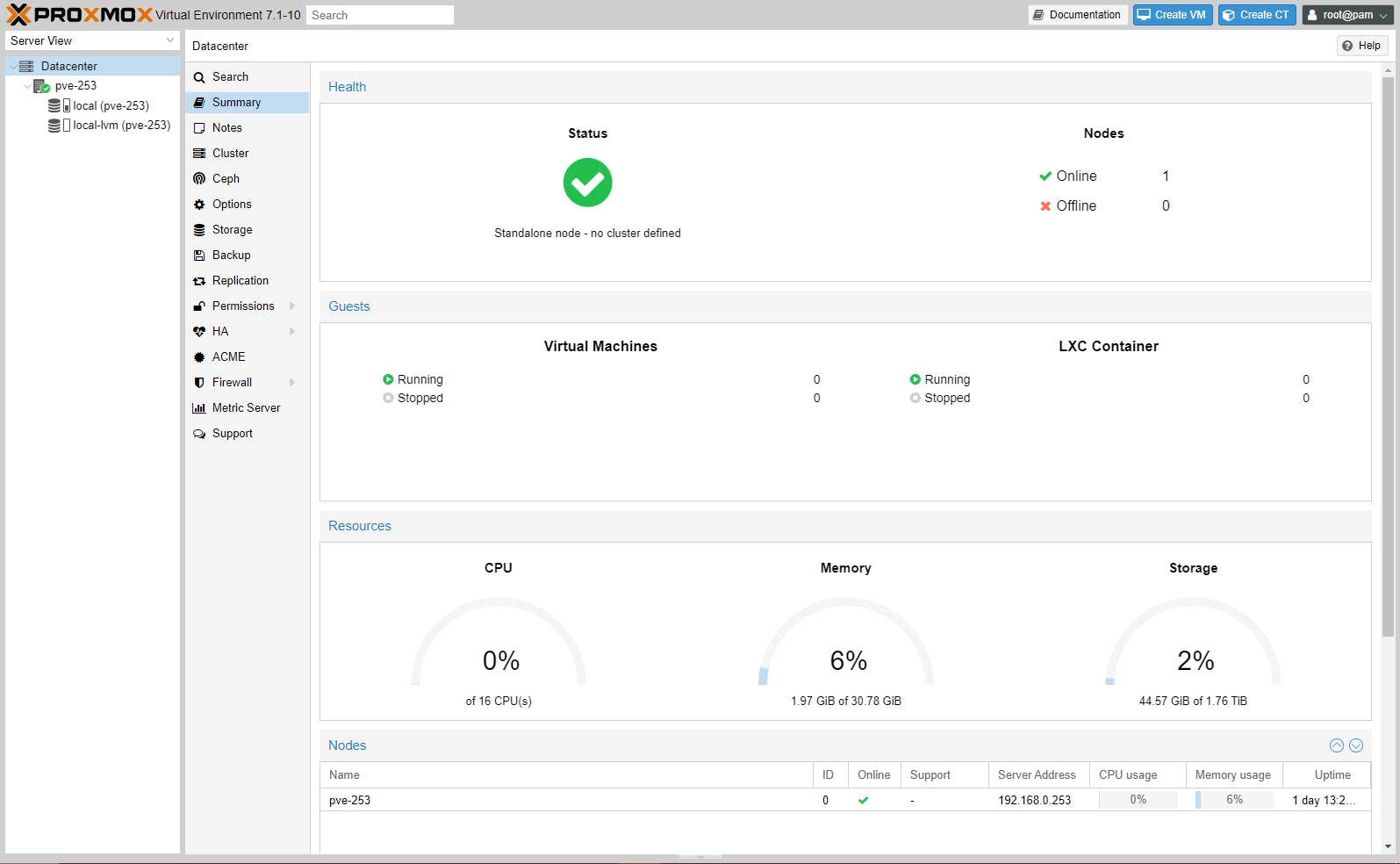
With a Proxmox VE setup running on a single node with no VMs or CTs setup, you can see below, using monitoring, the resource usage:
Datacenter
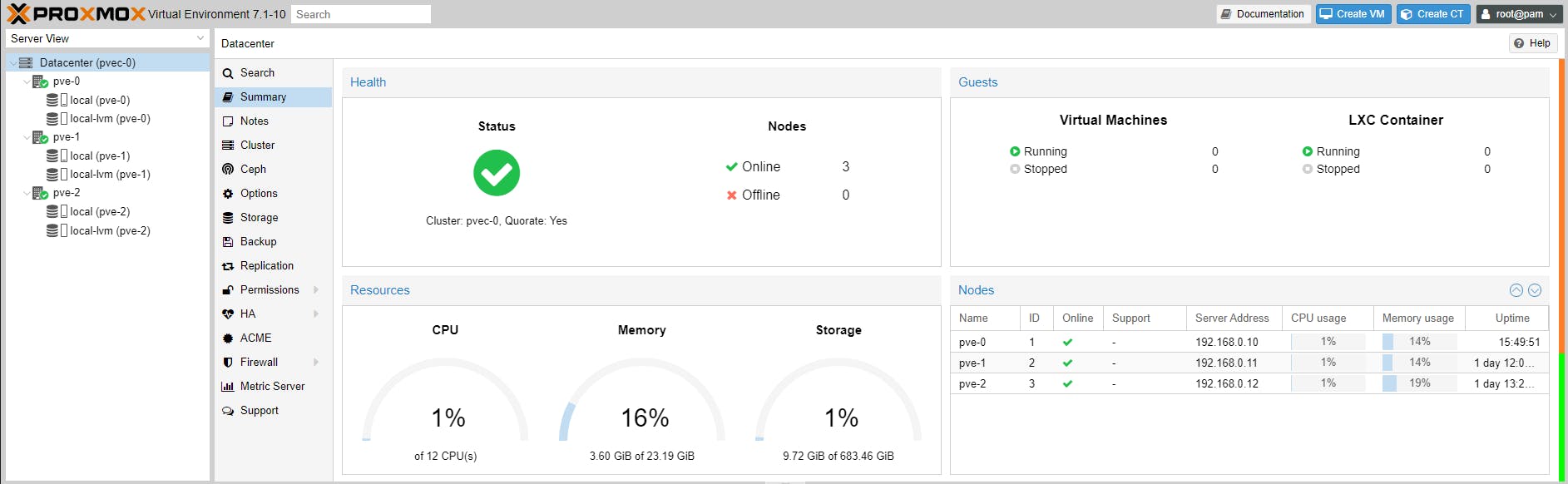
(The Datacenter can be considered an administrative unit associated with a GUI admin console. The Datacenter can manage only one node, which is the default behaviour, or can manage multiple nodes, if configured as a cluster. So from a single GUI admin console (e.g. https://192.168.0.253:8006) we can manage:
only one node, if there is no cluster,
or
- multiple nodes, if there is a cluster defined
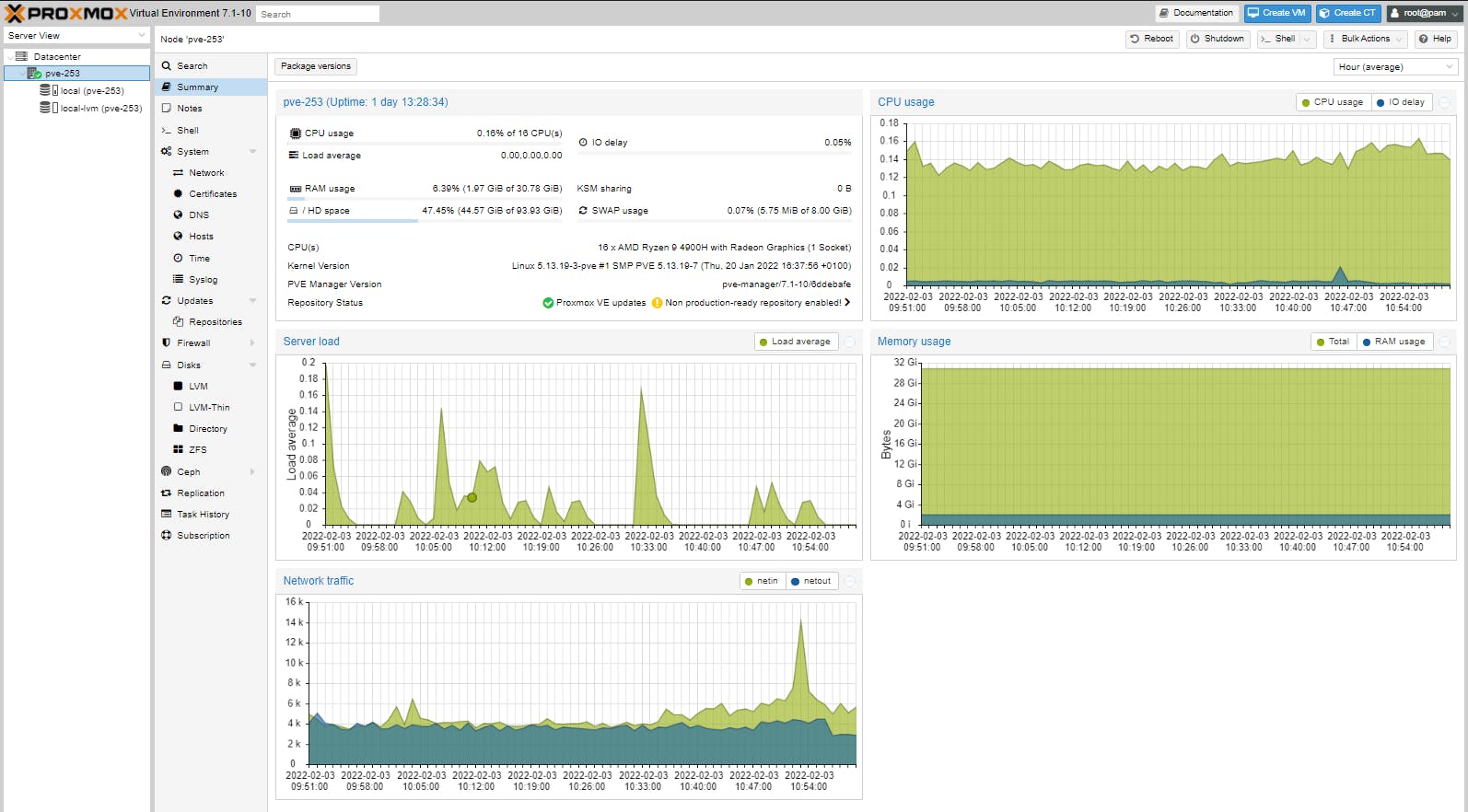
Node
(a physical PVE server, a bare-metal PVE installation)
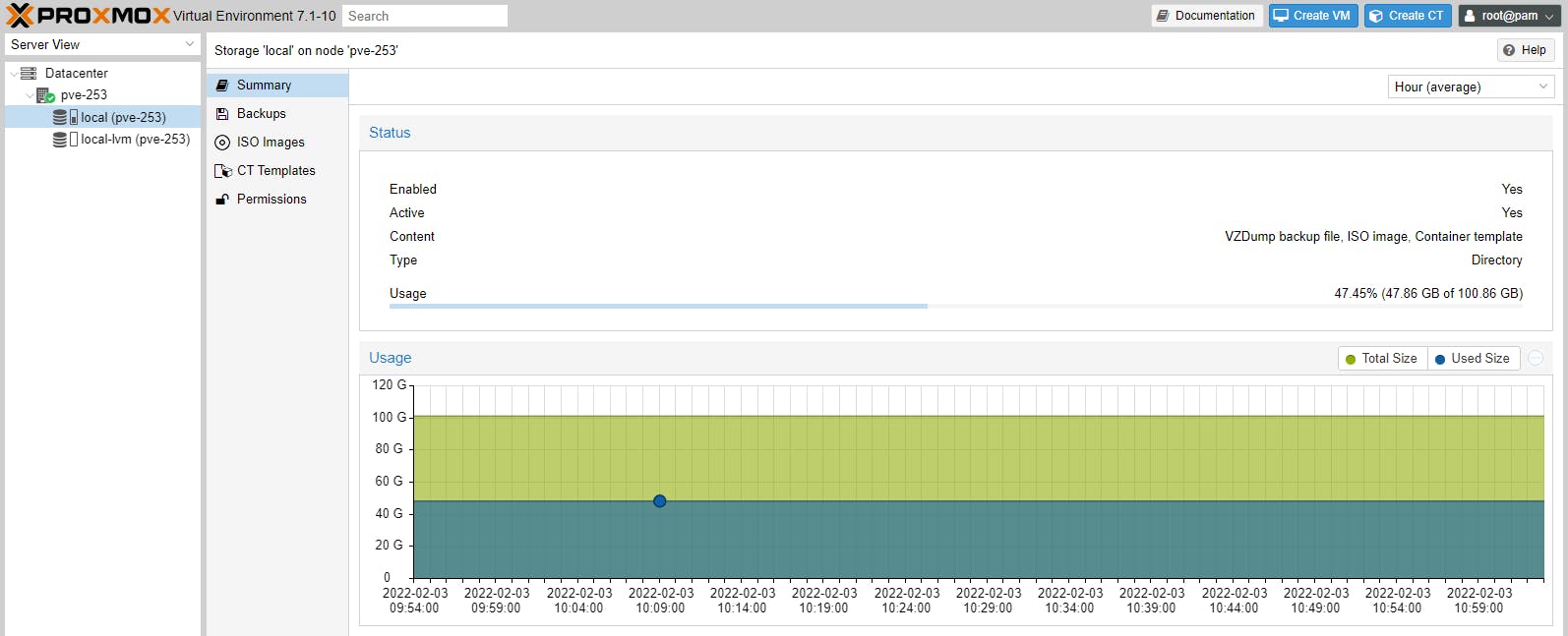
Storage
(only Backups, ISOs and CT Templates are stored in this location)
an example list of ISOs stored
Storage LVM
(only VM Disks and CT Volumes are stored in this location)
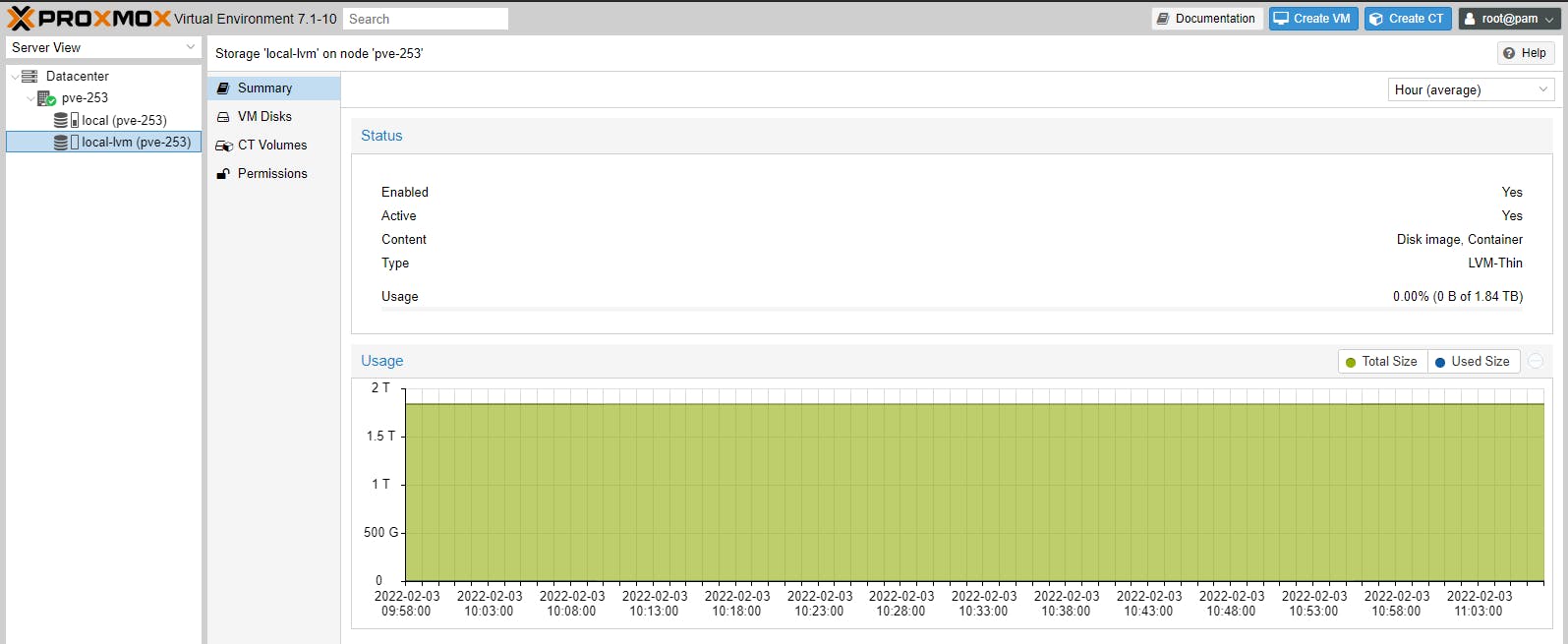
You see zero LVM storage used in the above screenshot because we have not setup any VMs or CTs.
For testing and learning you can install Proxmox in a paravirtualised environment running thee Proxmox VE VMs to test clustering and HA. With Proxmox this is easy to accomplish (we will run three VM Proxmox nodes using only one physical Proxmox node):
Install Proxmox on a physical machine - called a bare-metal install. Then create three VMs and install Proxmox again, on every VM. I suggest a minimum of 16 CPU threads, 32GB RAM and 2TB NVMe 3.0/4.0 SSD on the physical machine so things are not slow or crippled. We will cover this configuration scenario in a future article series (please consider subscribing to get an update when the articles get published).
For anyone wondering what such a setup would cost in terms of hardware, for a decent entry-level but respectable setup (a homelab, a small home-business, a small residence) you are looking around U$ 1,000/-
Please consider subscribing to my blog, as you will only ever get quality content; no time wasting, advertising, spamming or other unproductive activities/practices.
Please also consider visiting and subscribing to our YouTube channel; we have recently started posting videos.
We are committed to improving and enhancing over time.

